HTML Introduction
HTML is the standard markup language for Web pages. This tutorial follows the latest HTML5 standard. HTML is easy to learn - You will enjoy it!
What is HTML used for?
- create Web pages
- describe the structure of a Web page
- tell the browser how to display the content
What can HTML do?
- Document creation on the internet is dominated by HTML
- HTML is heavily used to embed hyperlinks within web pages
- At the elementary level in applications of HTML, queries can be set to utilize images, which are responsive in nature
- HTML5 has its application cache mechanism which would define how the browser manages offline situations
HTML Elements
- An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag
- Some HTML elements have no content (like the
<br>element). These elements are called empty elements. Empty elements do not have an end tag! - HTML elements can be nested (this means that elements can contain other elements). All HTML documents consist of nested HTML elements
HTML Elements
HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag. The content is everything between the start and end tags.
Example
<tagname>Content goes here...</tagname>HTML Attributes
All HTML elements can have attributes that provide additional information about elements. Attributes are always specified in the start tag and usually come in name/value pairs.
Attribute Basics
- All HTML elements can have attributes
- Attributes provide additional information about elements
- Attributes are always specified in the start tag
- Attributes usually come in name/value pairs like: name="value"
The href Attribute
The <a> tag defines a hyperlink. The href attribute specifies the URL of the page the link goes to:

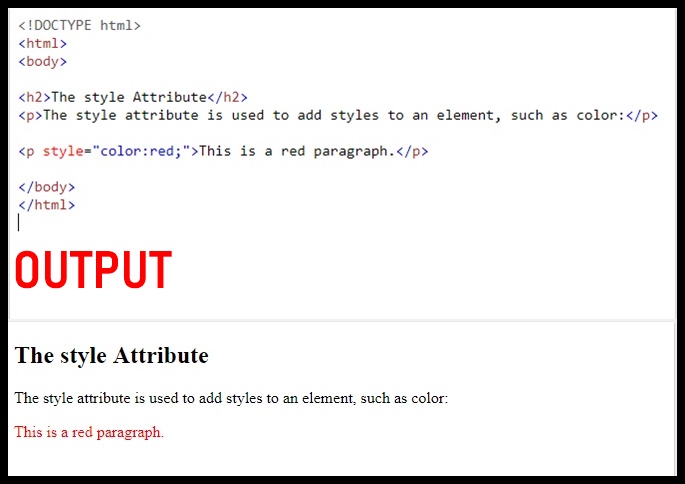
The style Attribute
The style attribute is used to add styles to an element, such as color, font, size, and more.
HTML Headings and Paragraphs
HTML headings are defined with h1 to h6 tags. Paragraphs are defined with the p tag.
HTML Headings
HTML headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags.
<h1> defines the most important heading. <h6> defines the least important heading.
HTML Paragraphs
The HTML <p> element defines a paragraph.
A paragraph always starts on a new line, and browsers automatically add some white space (a margin) before and after a paragraph.
HTML Styles
The HTML style attribute is used to add styles to an element, such as color, font, size, and more.
Common CSS Properties
- Use the style attribute for styling HTML elements
- Use background-color for background color
- Use color for text colors
- Use font-family for text fonts
- Use font-size for text sizes
- Use text-align for text alignment
HTML Links - Hyperlinks
HTML links are hyperlinks. You can click on a link and jump to another document. When you move the mouse over a link, the mouse arrow will turn into a little hand. Note: A link does not have to be text. A link can be an image or any other HTML element!
HTML Links - The target Attribute
By default, the linked page will be displayed in the current browser window. To change this, you must specify another target for the link.
The target attribute specifies where to open the linked document.
Target Attribute Values
_self- Default. Opens the document in the same window/tab as it was clicked_blank- Opens the document in a new window or tab_parent- Opens the document in the parent frame_top- Opens the document in the full body of the window
HTML Images
Images can improve the design and the appearance of a web page.
HTML Images Syntax
The HTML <img> tag is used to embed an image in a web page.
Images are not technically inserted into a web page; images are linked to web pages. The <img> tag creates a holding space for the referenced image.
The <img> tag is empty, it contains attributes only, and does not have a closing tag.
Required Attributes
src- Specifies the path to the imagealt- Specifies an alternate text for the image
HTML Iframes
An HTML iframe is used to display a web page within a web page.
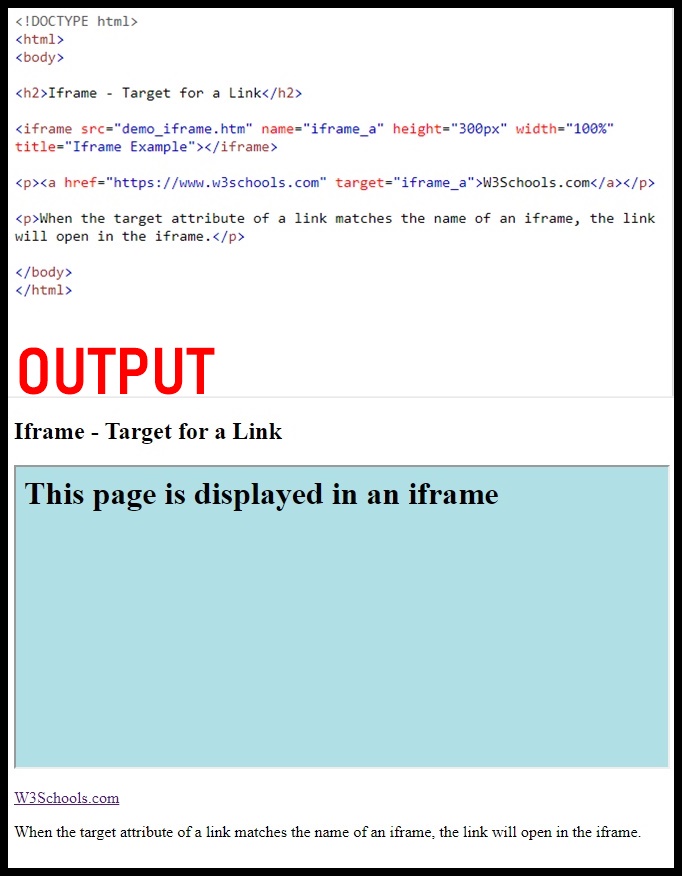
Iframe Attributes
- The HTML
<iframe>tag specifies an inline frame - The
srcattribute defines the URL of the page to embed - Always include a
titleattribute (for screen readers) - The
heightandwidthattributes specify the size of the iframe - Use
border:none;to remove the border around the iframe
HTML Lists
HTML lists allow web developers to group a set of related items in lists.
Unordered HTML List
An unordered list starts with the <ul> tag. Each list item starts with the <li> tag.
The list items will be marked with bullets (small black circles) by default.
Ordered HTML List
An ordered list starts with the <ol> tag. Each list item starts with the <li> tag.
The list items will be marked with numbers by default.
HTML Description Lists
HTML also supports description lists.
A description list is a list of terms, with a description of each term.
The <dl> tag defines the description list, the <dt> tag defines the term (name), and the <dd> tag describes each term.
HTML Tables
HTML tables allow web developers to arrange data into rows and columns.
Define an HTML Table
- The
<table>tag defines an HTML table - Each table row is defined with a
<tr>tag. Each table header is defined with a<th>tag. Each table data/cell is defined with a<td>tag - By default, the text in
<th>elements are bold and centered - By default, the text in
<td>elements are regular and left-aligned
HTML Block and Inline Elements
Every HTML element has a default display value, depending on what type of element it is.
There are two display values: block and inline.
Block-level Elements
A block-level element always starts on a new line and takes up the full width available (stretches out to the left and right as far as it can).
The <div> element is a block-level element.
The <div> element is often used as a container for other HTML elements.
Inline Elements
An inline element does not start on a new line and it only takes up as much width as necessary.
This is a <span> element inside a paragraph.
The <span> element is an inline container used to mark up a part of a text, or a part of a document.
